Introduction to Continuous Integration/Delivery (CI/CD).
Introduction to Continuous Integration/Delivery (CI/CD)
What is CI/CD ?
CI/CD is a way of developing software in which you’re able to release updates at any time in a sustainable way. When changing code is routine, development cycles are more frequent, meaningful and faster.
Continuous Integration is the practice of integrating code into a shared repository and building/testing each change automatically, as early as possible - usually several times a day.
Continuous Delivery adds that the software can be released to production at any time, often by automatically pushing changes to a staging system.
Continuous Deployment goes further and pushes changes to production automatically.
Why CI/CD ?
Continuous Integration
- Detects development as quickly as possiblie
- Fix while fresh in your mind
- Detect security issue earlier
- Reduces integration problems
- Smaller problems are easier to solved
- Don’t compound problems
- Allows teams to develop faster, with more confidence
Continuous Delivery
- Ensures that every change to the system is releasable
- Lowers risk of each release - makes releases “boring”
- Delivers value more frequently
- Get fast feedback on what users care about
How to use CI/CD ?
- Automate the build
- Make your build self-testing
- Keep the build fast
- Make the process transparent to everyone
- Maintain a single source repository
Tool of CI/CD
- Github Action
- Gitlab CI
- Jenkins
- etc
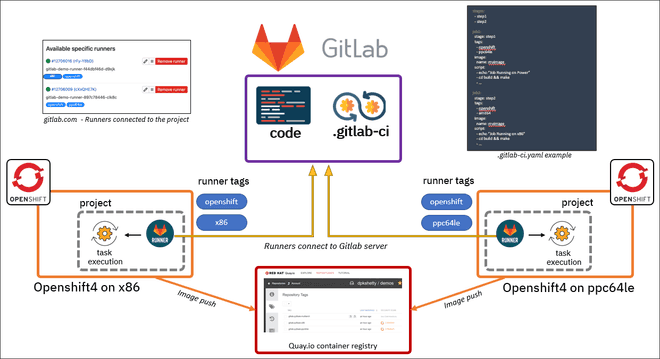
Gitlab CI
Concept
-
Pipelines are the top-level component of continuous integration, delivery, and deployment.
-
Jobs can output an archive of files and directories. This output is known as a job artifact.
-
Runner is an application that works with GitLab CI/CD to run jobs in a pipeline.
Pipeline
Stage
Stages, which define when to run the jobs. For example, stages that run tests after stages that compile the code.
Job
Jobs, which define what to do. For example, jobs that compile or test code.
Pipeline Declare
By default Gitlab CI will read .gitlab-ci.yml on your root Project directory.
Only accept
.ymlextention not.yaml
Variable
Variable Type
- Predefined CI/CD Variables ref
- Global/Instance Variable
- Group Variable
- Project Variable
.gitlab-ci.yml keyword reference
Most Used (by me)
Global
include
Import configuration from other YAML files.
stages
The names and order of the pipeline stages.
variables
Define CI/CD variables for all job in the pipeline.
workflow
Control what types of pipeline run.
Jobs
allow_failure
Allow job to fail. A failed job does not cause the pipeline to fail.
artifacts
List of files and directories to attach to a job on success.
before_script
Override a set of commands that are executed before job.
except
Control when jobs are not created.
extends
Configuration entries that this job inherits from.
image
Use Docker images.
needs
Execute jobs earlier than the stage ordering.
only
Control when jobs are created.
rules
List of conditions to evaluate and determine selected attributes of a job, and whether or not it’s created.
script
Shell script that is executed by a runner.
stage
Defines a job stage.
tags
List of tags that are used to select a runner.
variables
Define job variables on a job level.
when
When to run job.
Conclusion
Make First Pipeline
TL;DR:
- Define the stages,
- Define the jobs, and variables,
- Commit the file,
- Push!
Demo
.gitlab-ci.yml
variables:
DEBUG: ""
NAME: "Demo"
stages:
- build
- test
- deploy
debug:
stage: .pre
tags:
- golang
rules:
- if: $DEBUG == "true"
script:
- echo "REGISTRY=$REGISTRY"
- echo "GIT_WORKFLOW=$GIT_WORKFLOW"
- echo "CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE=$CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE"
- echo "CI_COMMIT_BRANCH=$CI_COMMIT_BRANCH"
- echo "CI_OPEN_MERGE_REQUESTS=$CI_OPEN_MERGE_REQUESTS"
- echo "CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME=$CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME"
- echo "CI_MERGE_REQUEST_IID=$CI_MERGE_REQUEST_IID"
- env
build-job:
stage: build
tags:
- golang
script:
- echo "Hello, $NAME!"
test-job1:
stage: test
script:
- echo "This job tests something"
test-job2:
stage: test
tags:
- golang
script:
- echo "This job tests something, but takes more time than test-job1."
- echo "After the echo commands complete, it runs the sleep command for 20 seconds"
- echo "which simulates a test that runs 20 seconds longer than test-job1"
- sleep 20
deploy-prod:
stage: deploy
tags:
- golang
script:
- echo "This job deploys something from the $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH branch."
environment: production